Core Resources’ ion exchange partner X GROUP Technologies (XGT) is advancing the commercialisation of its vanadium electrolyte process in South Africa. This innovative process is set to redefine the production of vanadium electrolyte for vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), leveraging cutting-edge technology and sustainable methods.
The XGT Process
The XGT process comprises three key steps:
- Low-Cost Extraction: Extracting vanadium from a range of secondary resources.
- Ion Exchange Resin Adsorption: Isolating, purifying, and concentrating vanadium through ion exchange resin.
- Eluate Modification: Adjusting the eluate solution to meet electrolyte specifications, including vanadium molarity (1.8M), valence charge (50% V4+ and 50% V3+), and sulphuric acid matrix (40%).
A State-of-the-Art Facility
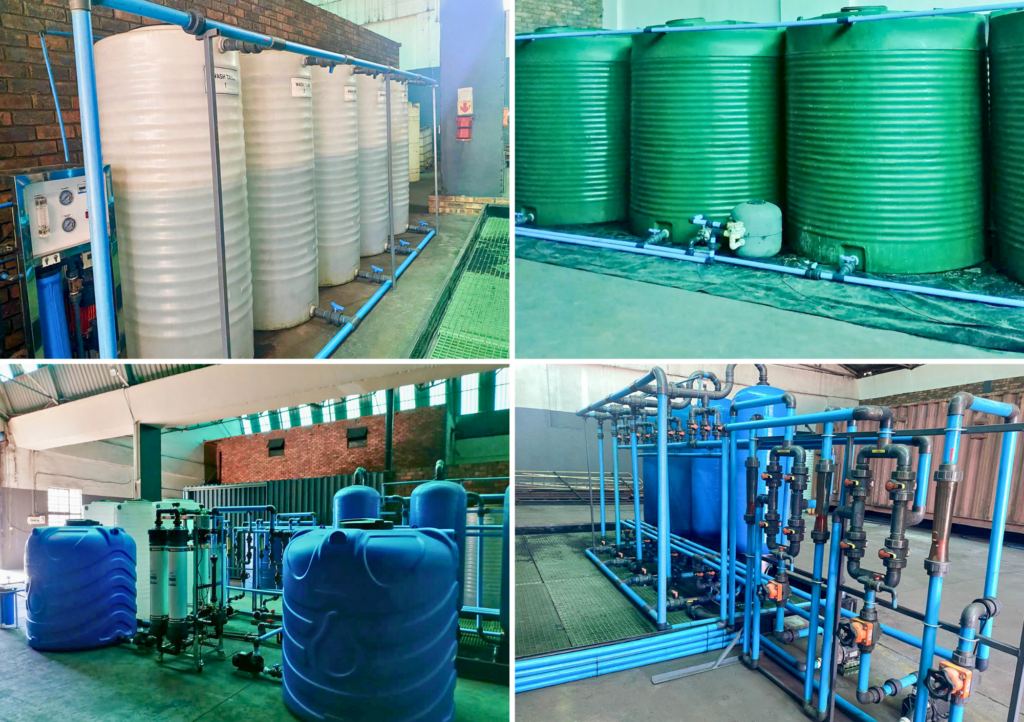
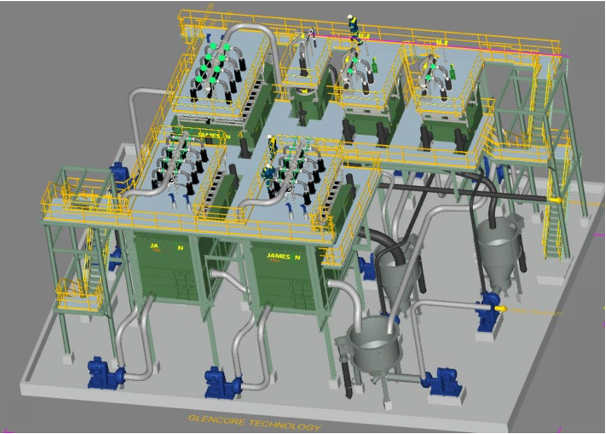
XGT constructed and commissioned its new facility in the final quarter of 2024. The ion exchange plant, shown in the image below, has a capacity of approximately 350Kl of electrolyte annually on a steady-state, continuous operations basis. The process will be ramped up to meet rising demand, with nameplate capacity expected by mid-2025.
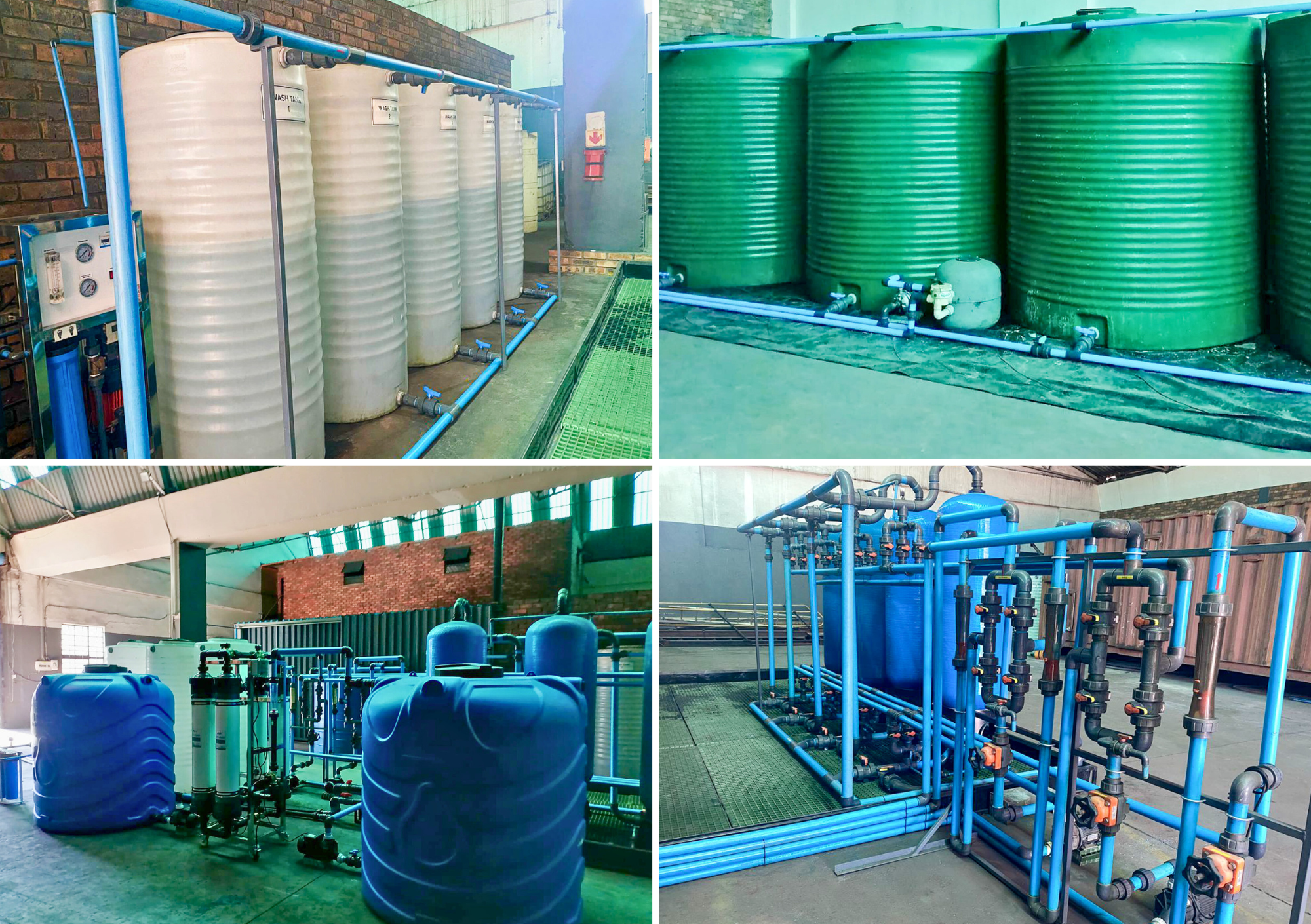

X Group Technologies ion exchange plant
A Competitive Edge in Electrolyte Production
The ability to prepare vanadium electrolyte within a hydrometallurgical flowsheet provides a significant competitive advantage. This approach differs from conventional methods, where premium-grade vanadium oxides (V2O3 and V2O5) are dissolved in sulphuric acid to prepare electrolyte.
Proven Technical Viability
The technical viability of the XGT process was confirmed in 2023 with the commissioning of a purpose-built demonstration plant, as shown below:

X GROUP Technologies Vanadyl sulphate demonstration plant
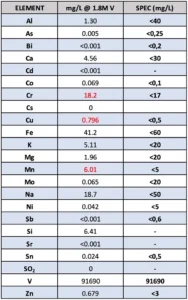
This proof-of-concept plant has delivered vanadyl sulphate product solutions of exceptional purity. Using ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry), XGT analysed the eluate composition, demonstrating compliance with stringent international electrolyte specifications. The table below compares XGT’s product analysis with one of the most demanding global standards.
Process Refinements for Purity
In 2024, XGT conducted further pilot-scale developments to ensure that base metal impurities remain well within specification limits. These refinements were executed in the experimental setup shown below:
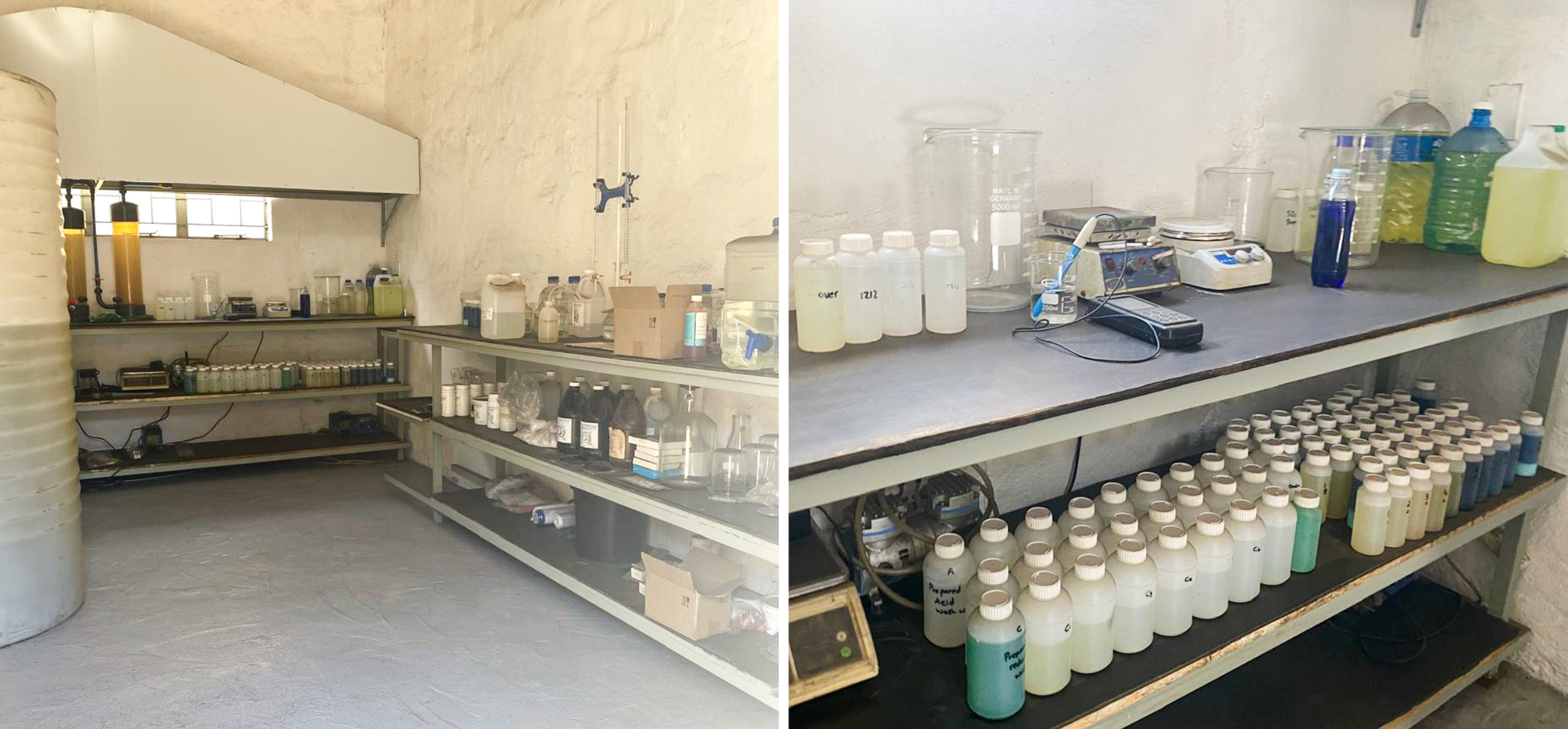

X GROUP Technologies Laboratory
Strategic Objectives and the Future
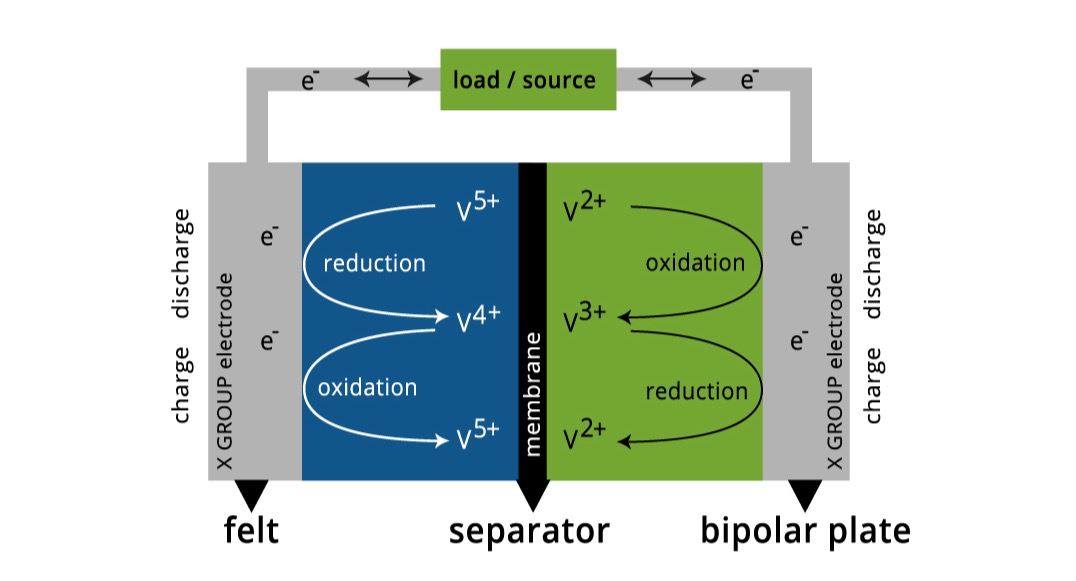
Since 2018, XGT has focused on producing ultra-pure vanadium electrolyte through a non-refractory process for direct use in VRFBs. The schematic diagram below illustrates the chemistry of these batteries:
The establishment of the XGT electrolyte facility represents years of dedicated innovation and process development by a specialised team.
About X GROUP
X GROUP is focused on processing secondary resources and effluents for recovery of metal values for conversion into valuable products. Its work in vanadium includes reprocessing hazardous vanadium tailings and process effluents, spent catalysts and fly-ash recovering remaining vanadium for conversion into sodium vanadate for AMV and V2O5, potassium vanadate for catalysts, vanadyl sulphate for APV or VRFB electrolyte and vanadyl chloride for dualacid VRFB batteries. Contact X GROUP here.
About Core Resources
Core Resources provides services in all aspects of metallurgical testing, process engineering, flowsheet development and site process services for the global mining industry. Core has approximately 50 professional staff, including chemical and process engineers, metallurgists and chemists, many of whom are shareholders in the business. Core has a global client base reflecting the world class expertise of its staff.
About Core IPEX
Core IPEX is a Queensland-based technology joint venture between the parties specifically for further refinement and commercialisation of X GROUP ion exchange technologies.
Contact us for more information.